The fashion and medical industries have experienced revolutionary changes in the past two decades, but few innovations are as transformative as the integration of 3D technology in the production of compact garments. Traditionally, compact or compression garments have been manufactured using manual design techniques, standardized sizes, and conventional textiles. However, the rise of advanced 3D modeling, body scanning, and additive manufacturing has opened the door to highly personalized, durable, and effective garments that serve both medical and lifestyle purposes. This article explores the role of 3D technology, its applications, advantages, challenges, and the promising future it holds for compact garment production worldwide. of using 3D technology in compact garment productio
Advantages of using 3D technology in compact garment production
Compact garments, often referred to as compression garments, have a long history in medicine and fashion. They were initially used to treat circulatory conditions and later expanded into post-surgical recovery, sports, and even body shaping. The production of compact garments has traditionally relied on tailoring and mass manufacturing, which often resulted in limited customization. For patients with specific medical needs or athletes requiring specialized support, this one-size-fits-all approach created gaps in performance and comfort.
With the advent of digital design, the process shifted towards more accurate sizing and higher-quality textiles. However, even with these improvements, the degree of personalization remained constrained until the widespread adoption of 3D technology.
The Rise of 3D Technology in Garment Design
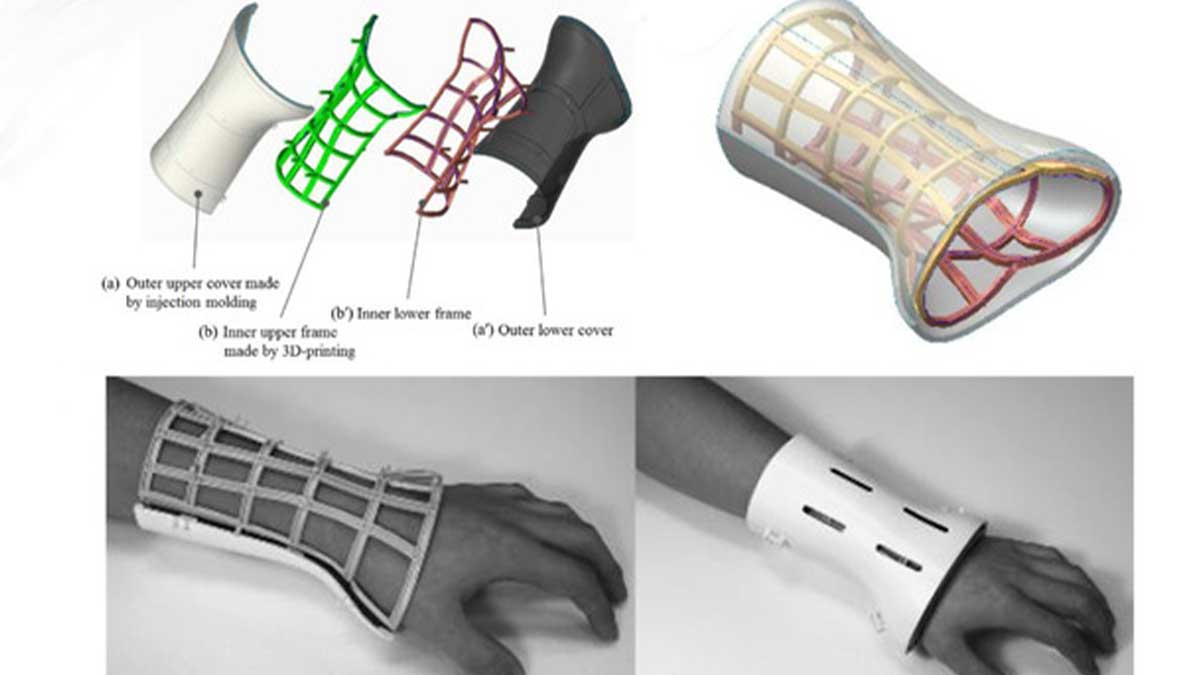
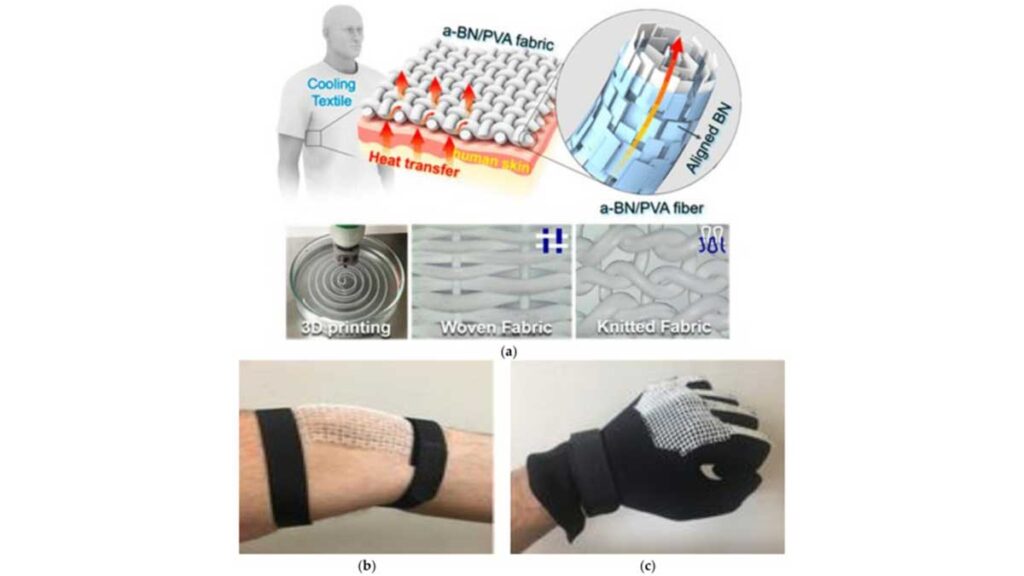
The introduction of 3D technology in the production of compact garments marked a significant leap forward. By combining body scanning systems, computer-aided design (CAD), and 3D printing, manufacturers can now create garments that perfectly fit the unique anatomy of each user. This precision not only enhances comfort but also boosts medical effectiveness.
Body scanning, in particular, has been a game-changer. Using 3D scanners, every contour of the body can be captured within seconds, producing accurate digital models. These models are then used to design compression garments tailored to an individual’s needs. In medical contexts, this ensures patients recovering from surgery or injury receive targeted support exactly where it is required.
Benefits of 3D-Enhanced Compact Garments
The adoption of 3D technology in the production of compact garments provides numerous benefits across industries. Customization stands at the forefront—patients and consumers can obtain garments that fit perfectly, reducing discomfort and increasing compliance with medical or fitness regimens.
Another major advantage lies in sustainability. 3D manufacturing allows for precise material use, drastically cutting down on waste. For companies striving to align with eco-friendly practices, this represents a crucial step forward.
Additionally, the integration of 3D techniques enables experimentation with new textiles, weaving patterns, and even smart fabrics embedded with sensors. These advancements expand the functionality of garments, offering not just compression but also monitoring capabilities.
Connecting Health and Comfort
One of the most compelling aspects of modern compact garments is how they bridge health benefits with user comfort. For example, medical experts highlight the benefits of compression garments in improving circulation, reducing swelling, and accelerating recovery. By applying consistent pressure to specific body areas, these garments enhance blood flow, supporting both athletes and patients.
The integration of 3D design ensures that this pressure is distributed with pinpoint accuracy. Instead of relying on general sizing, 3D-modeled garments account for individual body differences, ensuring that the therapeutic benefits are maximized without causing discomfort.
The Aesthetic Dimension
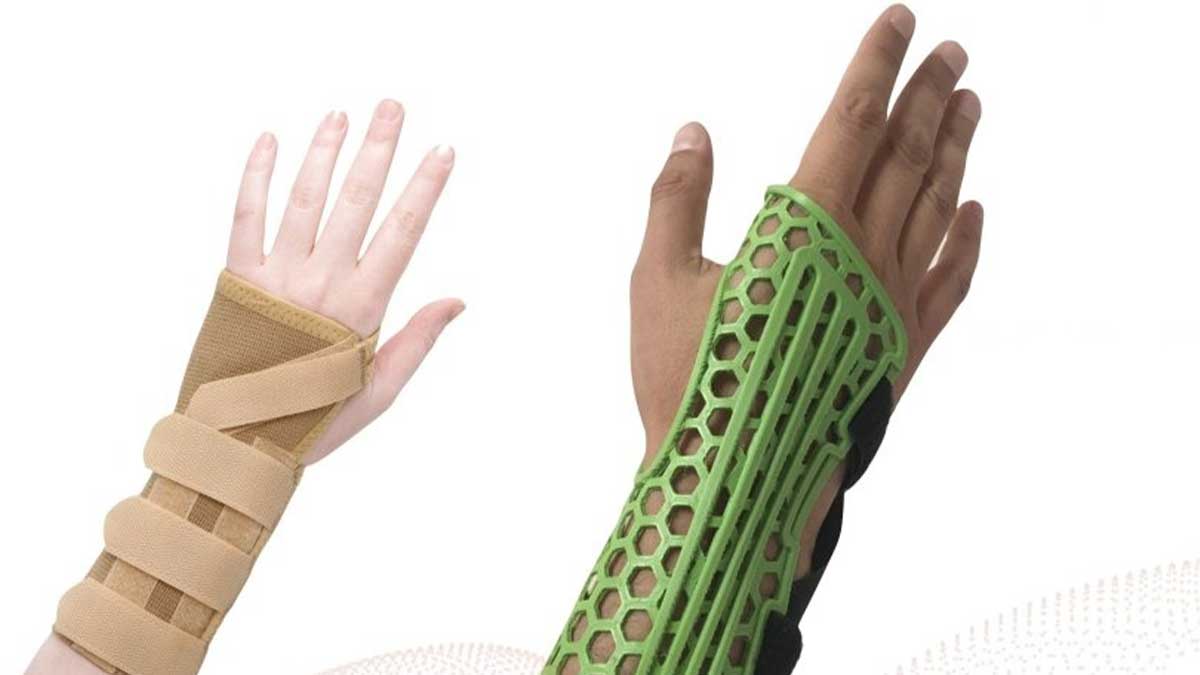

Beyond medical applications, lifestyle and aesthetic appeal play an increasingly important role in consumer decisions. With 3D design, compact garments are no longer just functional; they are stylish and versatile. Designers can incorporate fashion-forward elements while maintaining therapeutic functions, offering consumers garments that can be worn confidently in everyday settings. This dual purpose has significantly expanded the market for compact garments, attracting not only patients but also fitness enthusiasts and fashion-conscious individuals.
The Role of Research and Evidence
No innovation can gain widespread acceptance without supporting data. The effectiveness of 3D-based garment design is being validated through studies and scientific research. Clinical trials and engineering studies consistently demonstrate that 3D-tailored garments provide superior fit and more consistent compression compared to traditionally manufactured ones. This growing body of evidence reassures medical professionals and boosts consumer confidence, paving the way for mainstream adoption.
Specialized Applications
The production of compact garments using 3D technology has opened doors for specialized uses. In orthopedics, for instance, garments can be designed to provide graduated compression in precise regions, aiding in recovery from injuries. In oncology, patients undergoing surgery may benefit from garments engineered to minimize swelling and scarring.
Moreover, unique populations, such as patients with arthritis, are beginning to explore how these garments can improve daily living. While the topic may seem unconventional, discussions such as Why Compression Garments Are Beneficial for Arthritis Patients often highlight how targeted support and consistent compression reduce joint pain, swelling, and stiffness. With 3D customization, these benefits can be fine-tuned to individual needs.
Integration with Smart Technology
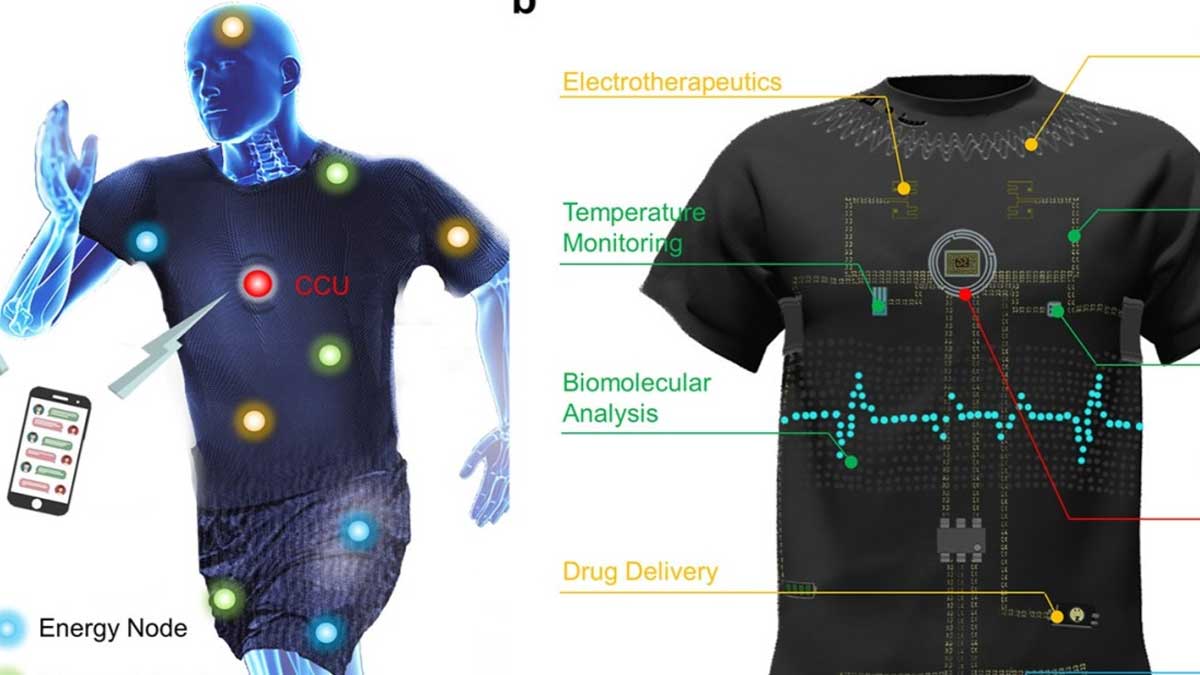
A fascinating aspect of 3D technology in the production of compact garments is its compatibility with smart textiles. Engineers are developing fabrics embedded with micro-sensors capable of tracking muscle activity, heart rate, and circulation. These smart garments transform traditional compression wear into diagnostic and preventive tools. Patients recovering at home, for example, could benefit from garments that continuously monitor their recovery and send updates to healthcare providers.
The potential synergy between 3D technology and digital health platforms is enormous. By merging physical support with data-driven insights, compact garments may become essential tools in personalized medicine.
Market Expansion and Consumer Demand
As technology evolves, consumer expectations also change. Today’s consumers value efficiency, personalization, and sustainability. The production of compact garments using 3D techniques aligns perfectly with these demands. Athletes seek improved performance and faster recovery, fashion enthusiasts demand style, and patients prioritize comfort and medical benefits. By addressing all these needs simultaneously, 3D-based garments are poised to dominate global markets.
Furthermore, public health campaigns emphasize The Benefits of Compression Garments for Health and Well-being, bringing broader awareness of their uses. By educating consumers about the therapeutic advantages, manufacturers strengthen demand across both clinical and non-clinical markets.
Challenges and Limitations
Despite its promise, 3D technology in the production of compact garments faces several hurdles. High initial costs of scanners, software, and 3D printers can be barriers for smaller companies. Additionally, training staff to use these technologies requires time and investment.
There is also the issue of accessibility. While major hospitals and athletic institutions can afford 3D-customized garments, broader populations may find them expensive. Balancing affordability with innovation remains one of the industry’s greatest challenges.
Lastly, ensuring long-term durability of 3D-printed textiles is still under examination. As with any new material, questions remain about longevity, especially when garments are subject to daily wear and washing.
Future Directions
Looking ahead, the future of 3D technology in the production of compact garments appears incredibly promising. Advancements in nanotechnology, biocompatible materials, and AI-driven design are likely to enhance personalization and efficiency further. Within the next decade, it may become standard for patients to undergo a quick body scan before being fitted with their recovery garment, just as easily as one might buy a tailored suit today.
The fusion of fashion, medicine, and technology will continue to evolve, blurring the lines between health products and lifestyle apparel. Compact garments may become everyday items, offering health benefits while integrating seamlessly into daily wardrobes.
Conclusion
The incorporation of 3D technology in the production of compact garments represents one of the most exciting intersections of healthcare, fashion, and technology. By enabling unparalleled customization, improving medical outcomes, and supporting sustainable practices, this innovation is reshaping industries and improving lives. From enhancing recovery for patients to boosting performance for athletes and elevating style for consumers, the applications are vast and transformative.
As more research emerges and technology becomes accessible, compact garments created with 3D methods may well become the gold standard worldwide. For now, they symbolize a bold step into the future—a future where garments do not just clothe the body but actively contribute to health, confidence, and well-being.